Recently, a research report published in the international core journal “Toxicology Reports” pointed out that after smokers switch to e-cigarettes or heat-not-burn products, their exposure to harmful substances is greatly reduced, and e-cigarettes reduce harm The effect is better than heat-not-burn products.

The report was published in the core journal “Toxicological Research”
The report pointed out that smoking is the main cause of many diseases. Although the smoking rate has declined in the past 50 years, the health risks caused by smoking are still high. Therefore, it is particularly important to establish a comprehensive set of scientific evidence for harm reduction products such as electronic cigarettes and heating non-combustion products.
The study selected 148 smokers as the observation objects of the clinical trial. These smokers were randomly divided into four groups based on the use of traditional cigarettes, electronic cigarettes, heating non-combustible products and complete cessation of smoking.
According to the list of harmful or potentially harmful substances listed by the US Food and Drug Administration, the researchers analyzed the contents of 16 components in the subjects’ urine and exhaled air. These harmful substances include exhaled air, carbon monoxide and cotinine (nicotine metabolites) in the urine.
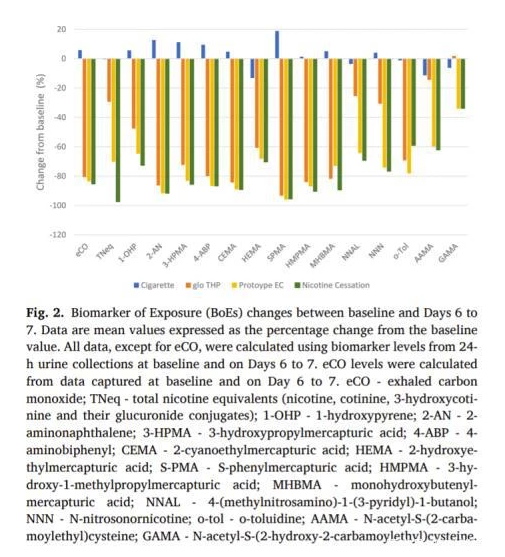
Experimental results showed that smokers who switched to electronic cigarettes or heated non-combustible products greatly reduced their exposure to harmful substances. The content of certain harmful substances in the metabolites is similar to that of completely quitting smoking. And it can be found that compared with heating non-combustion products, electronic cigarettes have a higher degree of harm reduction.
For example, the content of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the exhaled air of e-cigarette users is 64.7% lower than that of smokers, and the content of acrylonitrile is reduced by 89%. Compared with smokers, the levels of tobacco-specific nitrosamine (TSNA) metabolites NNAL and NNN in the urine of e-cigarette users decreased by 64.2% and 74.1%, respectively.
It is worth noting that tobacco-specific nitrosamines are one of the most important carcinogens and harmful substances in secondhand smoke of traditional cigarettes. This conclusion also coincides with the paper published by researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in 2020. The study once pointed out that the content of NNAL in the urine of e-cigarette users is only 2.2% of cigarette smokers, which proves that e-cigarettes do not have the second-hand smoke problem of traditional cigarettes.
At the end of the report, the author pointed out that governments and research institutions in many countries are adopting various tobacco control policies to encourage smokers to quit, provide smokers with long-term treatment, or recommend them to use nicotine replacement therapy, but this is for smokers to quit smoking completely. Still very difficult. At present, e-cigarettes have been proven to be an effective method of continuous smoking cessation. For smokers who cannot completely quit smoking, the use of e-cigarettes to reduce the harm of tobacco may be a practical method of tobacco control and harm reduction.



















Leave a Reply